Predicting the popularity of a pop song could be achieved by using state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms, say University of Bristol (UK) computer scientists who have created software to interpret the various musical factors that make a song a hit. The research team, led by Dr Tijl de Bie, have created thehttp://scoreahit.com/ website which details their work and provides an analysis of pop music’s evolution over the years.
Previously, researchers at Emory University had worked on predicting the likelihood of a song’s success using MRI scans from the brains of music listeners. Eschewing the human component, the new software makes use of musical features such as, tempo, time signature, song duration and loudness, as well as more complex traits such as harmonic simplicity, chord sequence and how “noisy” the song is.
The Bristol team found they could classify a song into a “hit” or “not hit” with an accuracy rate of 60 percent; specifically, whether a song will make it to the top five, or if it will never reach above position 30 on the top 40 singles chart.
“Musical tastes evolve, which means our ‘hit potential equation’ needs to evolve as well. Indeed, we have found the hit potential of a song depends on the era. This may be due to the varying dominant music style, culture and environment,” noted De Bie, a senior lecturer in Artificial Intelligence.
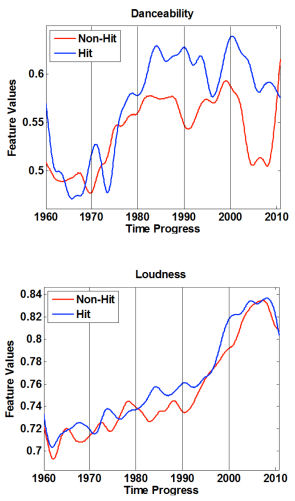
- Before the eighties, the danceability of a song was not very relevant to its hit potential. But from then on, danceable songs were more likely to become a hit. Also the average danceability of all songs on the charts increased suddenly in the late seventies.
- In the eighties, slower musical styles (70-89 beats per minute) such as ballads were more likely to become hits.
- The prediction accuracy of the researchers’ hit potential equation varies over time. It was particularly difficult to predict hits around 1980. The equation performed best in the first half of the nineties and from the year 2000. This, according to De Bie, suggests that the late seventies and early eighties were particularly creative and innovative periods of pop music composition.
- From the nineties onward hits more commonly have simpler, binary, rhythms such as 4/4 time.
- All songs on the chart are becoming louder. Additionally, the hits are relatively louder than the songs that dangle at the bottom of the charts, reflected by a strong weight for the loudness feature.
Related:
Discuss this article in our forum
Study identifies key aspects of music that evoke emotions in brain
This Is Your Brain On Jazz
Human music and speech biologically linked
Schizophrenic computer models mental illness















![FUNKO POP ROCKS: MICHAEL JACKSON 352 (1984 GRAMMYS) [DIAMOND EXCLUSIVE] NEW picture](/store/img/g/YxMAAOSwgUplkFb6/s-l225/FUNKO-POP-ROCKS-MICHAEL-JACKSON-352-1984-GRAMMYS-D.jpg)
Comments are closed.