
Scientists have identified a key region of the brain which encourages us to be adventurous. The region, located in a primitive area of the brain, is activated when we choose unfamiliar options, suggesting an evolutionary advantage for sampling the unknown.
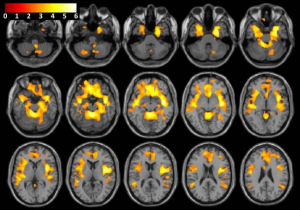
The experimental evidence was gained by University College London (UCL) researchers who carried out tests on volunteers while using an fMRI scanner to observe the brain at work. The volunteers were shown a selection of images, which they had already been familiarized with. Each image had a unique probability of reward attached to it and over the course of the experiment the volunteers would be able to work out which selection would provide the highest rewards. However, when unfamiliar images were introduced, the researchers found that volunteers were more likely to take a chance and select one of these options than continue with their familiar (and safer) options.
“Seeking new and unfamiliar experiences is a fundamental behavioral tendency in humans and animals,” said Dr Wittmann. “It makes sense to try new options as they may prove advantageous in the long run. For example, a monkey who chooses to deviate from its diet of bananas, even if this involves moving to an unfamiliar part of the forest and eating a new type of food, may find its diet enriched and more nutritious.”
The ventral striatum is one of the key areas involved in processing rewards in the brain. Although the researchers cannot say definitively from the fMRI scans how novelty seeking is being rewarded, Dr Wittmann believes it is likely to be through dopamine release.
Interestingly, however, whilst rewarding the brain for making novel choices may prove advantageous in encouraging us to make potentially beneficial choices, it may also make us more susceptible to exploitation.
“I might have my own favorite choice of chocolate bar, but if I see a different bar repackaged, advertising its ‘new, improved flavor’, my search for novel experiences may encourage me to move away from my usual choice,” says Dr Wittmann. “This introduces the danger of being sold ‘old wine in a new skin’ and is something that marketing departments take advantage of.”
Related:
This Is Your Brain On Jazz
Gene Mutation Responsible For Human Intelligence Tracked Down?
Risky Business Explained














Comments are closed.