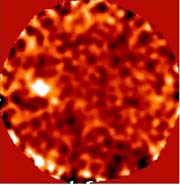
Data from the Hubble Space Telescope has been used to generate a spatial map demonstrating the clumped substructure of dark matter inside clusters of galaxies. Clusters of galaxies (about a million, million times the mass of our sun), are typically made up of hundreds of galaxies bound together by gravity. About 90 percent of their mass is dark matter. The rest is ordinary atoms in the form of hot gas and stars.
Although little is known about it, cold dark matter is thought to have structure at all magnitudes. Theoretical models of the clumping properties were derived from detailed, high resolution simulations of the growth of structure in the Universe. Although previous evidence supported the “concordance model” of a Universe mostly composed of cold, dark matter, the predicted substructure had never been detected.
In the study – appearing in Astrophysical Journal Letters – researcher Priyamvada Natarajan at Yale and her colleagues demonstrated that, at least in the mass range of typical galaxies in clusters, there is an excellent agreement between the observations and theoretical predictions of the concordance model. Using gravitational lensing made it possible for the observers to visualize light from distant galaxies as it bent around mass in its way. This allowed the researchers to measure light deflections that indicated structural clumps in the dark matter.

















Comments are closed.