27 July 2011
Scientists quantify critical-mass required for spread of ideas
by Kate Melville
If just 10 percent of the population holds an unshakable belief, their belief will always be adopted by the majority, say cognitive scientists from the Rensselaer Institute. The findings, appearing in Physical Review E, have broad implications for the study of innovation, the spread of ideas and the movement of political ideals.
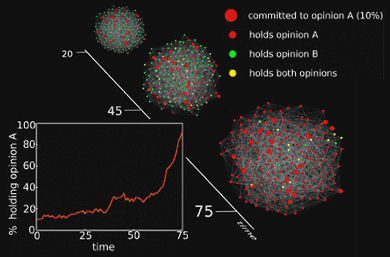
"When the number of committed opinion holders is below 10 percent, there is no visible progress in the spread of ideas. It would literally take the amount of time comparable to the age of the universe for this size group to reach the majority," said Rensselaer's Boleslaw Szymanski. "Once that number grows above 10 percent, the idea spreads like flame."
To identify the tipping point, Szymanski and his team developed computer models of various types of social networks. One of the networks had each person connect to every other person in the network. The second model included certain individuals who were connected to a large number of people, making them opinion hubs or leaders. The final model gave every person in the model roughly the same number of connections. The initial state of each of the models was a sea of traditional-view holders. Each of these individuals held a view, but were also, importantly, open minded to other views.
Once the networks were built, the scientists then "sprinkled" in some true believers throughout each of the networks. These people were completely set in their views and unflappable in modifying those beliefs. As those true believers began to converse with those who held the traditional belief system, the tides gradually, and then very abruptly, began to shift.
An important aspect of the finding is that the percent of committed opinion holders required to shift majority opinion does not change significantly regardless of the type of network in which the opinion holders are working. In other words, the percentage of committed opinion holders required to influence a society remains at approximately 10 percent, regardless of how or where that opinion starts and spreads.
"In general, people do not like to have an unpopular opinion and are always seeking to try locally to come to consensus. We set up this dynamic in each of our models," explained co-researcher Sameet Sreenivasan. To accomplish this, each of the individuals in the models "talked" to each other about their opinion. If the listener held the same opinions as the speaker, it reinforced the listener's belief. If the opinion was different, the listener considered it and moved on to talk to another person. If that person also held this new belief, the listener then adopted that belief.
"As agents of change start to convince more and more people, the situation begins to change," Sreenivasan said. "People begin to question their own views at first and then completely adopt the new view to spread it even further. If the true believers just influenced their neighbors, that wouldn't change anything within the larger system, as we saw with percentages less than 10."
The researchers are now looking for partners within the social sciences and other fields to compare their computational models to historical examples.
Related:
Evolution And The Hive Mind
War cheaper, more popular than ever
Sex selection gender skew in East raises concerns
Modern concerns echoed in ancient papyrus
Source: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
