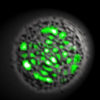
Researchers at Stanford have built a synchronous computer that operates using the unique physics of moving water droplets. The droplet processor is significantly slower than an electronic computer, but the research team says that speed is not their aim; rather, they want to develop a completely new class of computers that can precisely control and […]