
Scientists conducting a series of experiments on the International Space Station say that some micro-organisms can survive for long periods exposed to the hostile environment of outer space. The findings, published in theAstrobiology Journal, lend weight to the concept of panspermia, where life on Earth emerged from bacterial colonies transported on comets and asteroids.
The experiments were designed to see whether bacterial hitchhikers on spacecraft were hardy enough to survive in space andcontaminate other planets. Currently, spacecraft landing on Mars or other planets where life might exist must meet requirements for a maximum allowable level of microbial life (known as bioburden). These acceptable levels were based on studies of how various life forms survive exposure to the rigors associated with space travel.
“If you are able to reduce the numbers to acceptable levels, a proxy for cleanliness, the assumption is that the life forms will not survive under harsh space conditions,” explains NASA’s Kasthuri J. Venkateswaran. But that assumption may not hold up, as it seems some microbes are hardier than expected.
Venkateswaran says spores of Bacillus pumilus SAFR-032 have especially high resistance to techniques used to clean spacecraft, such as UV radiation and peroxide treatment. In one of the recent experiments, Bacillus pumilus SAFR-032 spores were exposed for 18 months on the European Technology Exposure Facility (EuTEF, pictured), a test facility mounted outside the space station.
“We wanted to see what would happen in real space, and EuTEF gave us the chance,” says Venkateswaran. “To our surprise, some of the spores survived for 18 months.”
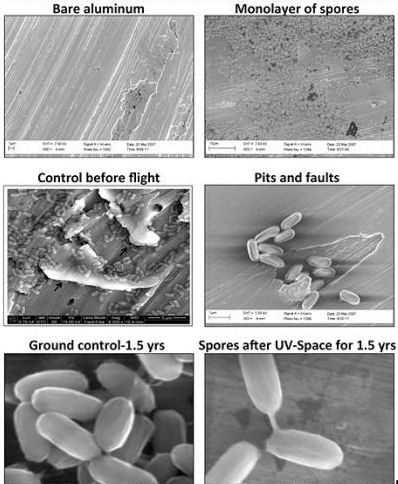
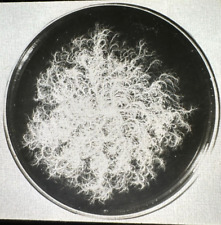
In another experiment, scientists placed rock-colonizing cellular organisms in the EuTEF facility for 1.5 years, further testing a theory of how organisms might move from one planet to another, known as lithopanspermia.
In this scenario, rocks ejected from a planet by impact with, for example, a meteor, carried organisms on their surface through space and then landed on another planet, bringing that life with them. For this investigation, researchers selected organisms especially adapted to cope with the environmental extremes of their natural habitats on Earth, and found that some are also able to survive in the even more hostile environment of outer space. Lithopanspermia would require thousands or even millions of years, much longer than the experiment’s duration, but the results provide the first evidence of the hardiness of these organisms in space and suggest the possibility that space-traveling rocks could carry life between planets.
Related:
Discuss this article in our forum
DNA Precursors In Meteorite Confirmed As Extraterrestrial
One-way Mars missions mooted
Curiosity rover finally demystifies radiation hazards on Mars
“Hot” Comets The Source Of Life?













Comments are closed.