All information from below post was used by Tolman in his brightness test.At the end of post I showed link to his oryginal testHow looks single bulb in space ? 
More far from place where
the signal started = lower intensity of signal
( "lower brightness" )
1R = X , 2R = X/4 , 3R = X/9
X- brightness, R- radius the same energy portion but different area
What is happen if Bulb is moving in space
below oryginal Doppler's drawing

The bulb is sending 3D wave from each new point in space where is ,was, and will be ..
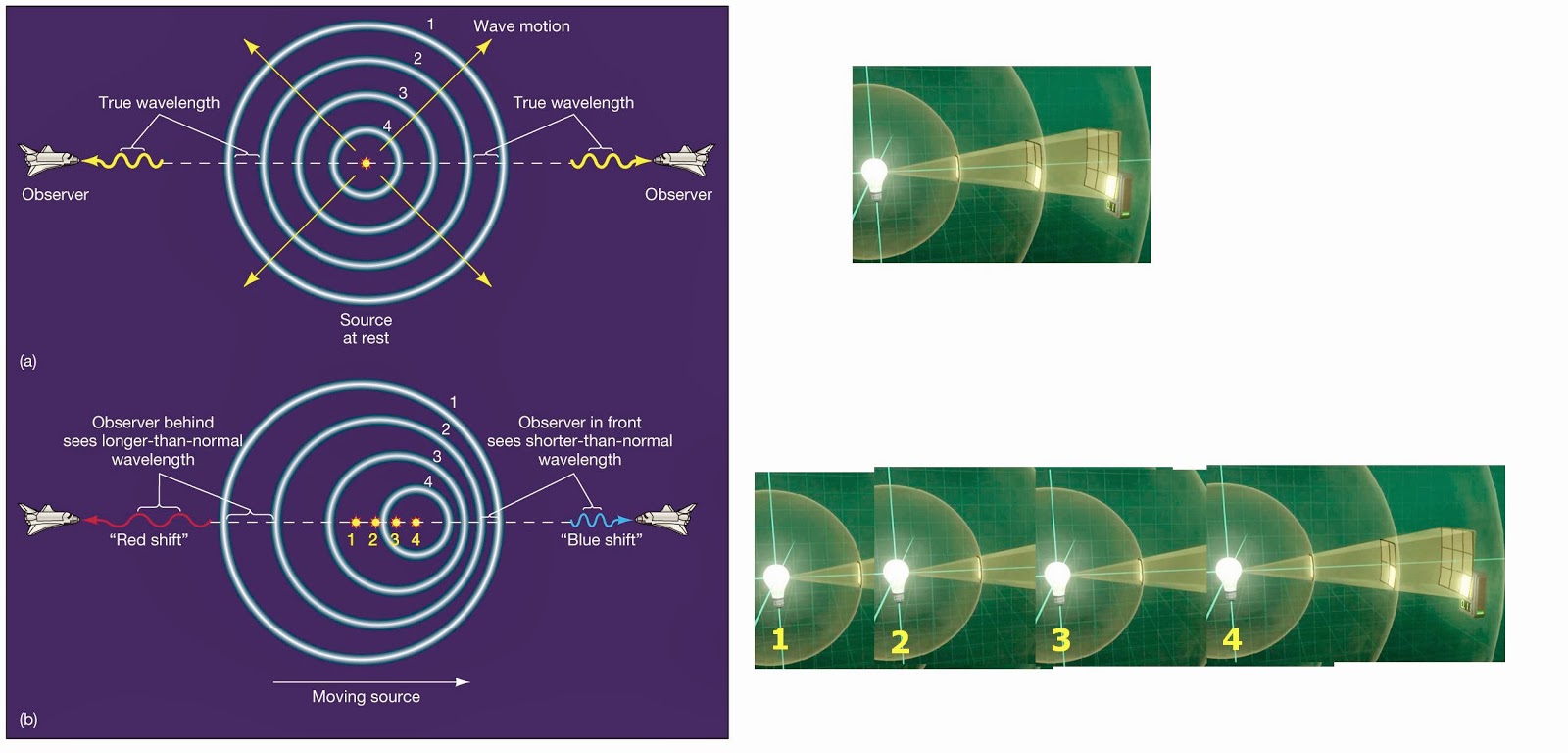 Above I presented facts from books below experiment proposition
Above I presented facts from books below experiment proposition 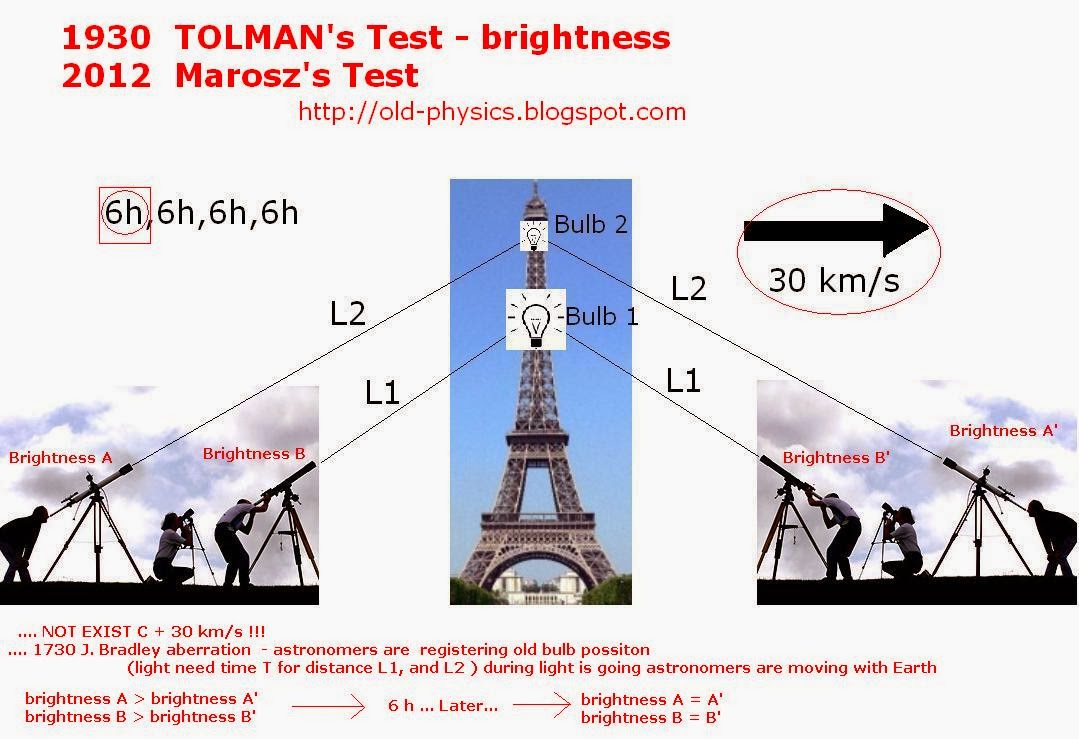
Bulb is moving in space ( Light speed is only C not C+30 km/s)
Light need short time for distance L1 or L2
We have two astronomers that at one and the same time are waching the same bulb . Problem is witch one is more closer the place where bulb was in past ?. ( they are waching old apparent position of the bub below important animation )
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/6/6d/Aberrationlighttimebeaming.gif I want to find relation between brightness ( signal's intensity and motion )
 Problem that above test can solve ?HISTORY
Problem that above test can solve ?HISTORY " Galileo postulated his relativity hypothesis: any two observers moving at constant speed and direction with respect to one another will obtain the same results for all mechanical experiments (it is understood that the apparatuses they use for these experiments move with them).
This idea has a very important consequence: velocity is not absolute. This means that velocity can only be measured in reference to some object(s), and that the result of this measurment changes if we decide to measure the velocity with respect to a diferent refernce point(s). Imagine an observer traveling inside a windowless spaceship moving away from the sun at constant velocity. Galileo asserted that there are no mechanical experiments that can be made inside the rocket that will tell the occupants that the rocket is moving .
The question ``are we moving'' has no meaning unless we specify a reference frame (are we moving with respect to that star'' is meaningful). This fact, formulated in the 1600's remains very true today and is one of the cornerstones of Einstein's theories of relativity."
 1930 Tolman surface brightness test
1930 Tolman surface brightness test
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tolman_surface_brightness_testmore tests
http://old-physics.blogspot.de/ author
Maciej Marosz
Engineer and Inventor
http://tesla4.blogspot.com





