We all know about Einstein idea
*****
Einstein was intrigued by the fact that the two ways of measuring mass come up with the same value, gravitational mass and intertial mass. The fact that the two masses are the same is why Galileo found that all things fall to the earth with the same acceleration.
*****
Small problem for above idea
.. mass m
.
.
...20 meters (above the Earth level)
.
.
.
.P1>
....^
....P2
.. EARTH
mass m is going to Earth ( kinetic energy mass m rise up )
P1 = pusser 1 ( perpendicular )
P2 = pusser 2 (opposite parallel pusser)
P1 pusser will feel lower Inertial mass m ( more easy is push mass m perpendicular to motion )
P2 pusser will feel different Inertial forces it will work
opposite to mass m
ABSOLUTE SPACE ? RESPECT TO WHAT WE CAN MEASURE INERTIA
( Above example is not so good model )
APPARENT POINT ??
= point where mass m was in past
= point that is not moving (full virtual point)
Please see animation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Aberrationlighttimebeaming.gif What is it motion ? how to evaluate inertia ( symetry and asymetry )
Everyone know many tests that made Sir Newton
I'm absolutly sure that You know below experiment
Pipe dynamite and two masses m
----------------------
m-----dynamite-------m ------20 km/s ------>
----------------------
observer 2 (is moving with pipe and earth )
Observer 1 - roped with apparent point
after explosion Observer 1
(for him ) mass m left slown down delta V mass right accelerate delta V
after explosion Observer 2
(for him ) mass m right and m left is moving the same speed
delta V
Question ? : Observer 2 is able or not able regognize and measure how many enrgy from dynamite escape to left mass and how many energy from dynamite take mass m right ?
below graph I made respect to apparent point for rocket
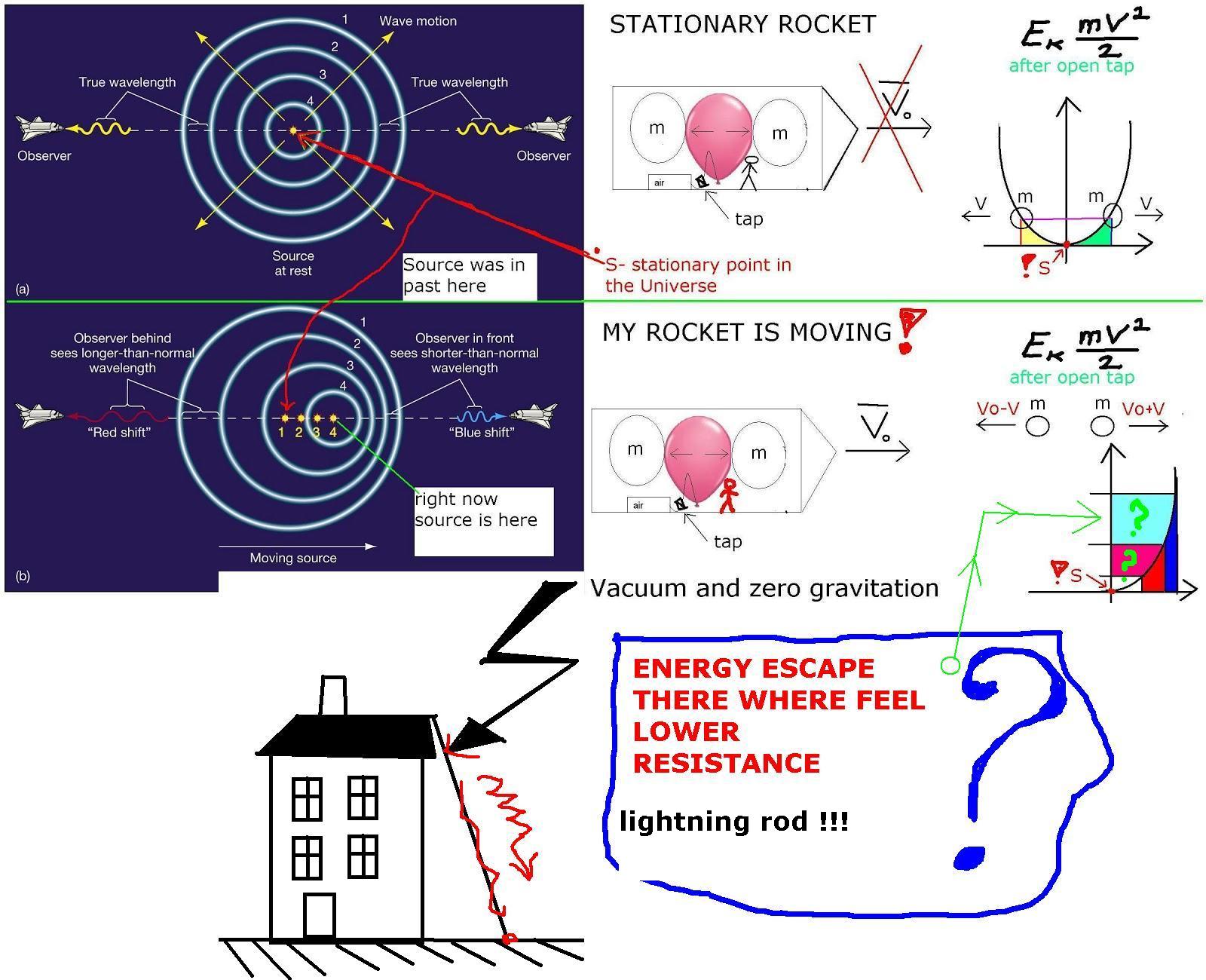
BELOW PARAGRAPH WE HAVE IN EACH BOOK ( physics )
" Galileo postulated his relativity hypothesis: any two observers moving at constant speed and direction with respect to one another will obtain the same results for all mechanical experiments (it is understood that the apparatuses they use for these experiments move with them).
This idea has a very important consequence: velocity is not absolute. This means that velocity can only be measured in reference to some object(s), and that the result of this measurment changes if we decide to measure the velocity with respect to a diferent refernce point(s). [c


