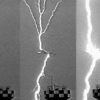
Over the last decade, scientists learnt that thunderstorms are capable of generating brief but powerful bursts of gamma-rays calledterrestrial gamma-ray flashes (TGFs). These flashes of gamma-rays are so bright they can blind instruments many hundreds of kilometers away in outer space. Because they can originate at the same altitudes at which commercial aircraft fly, scientists […]